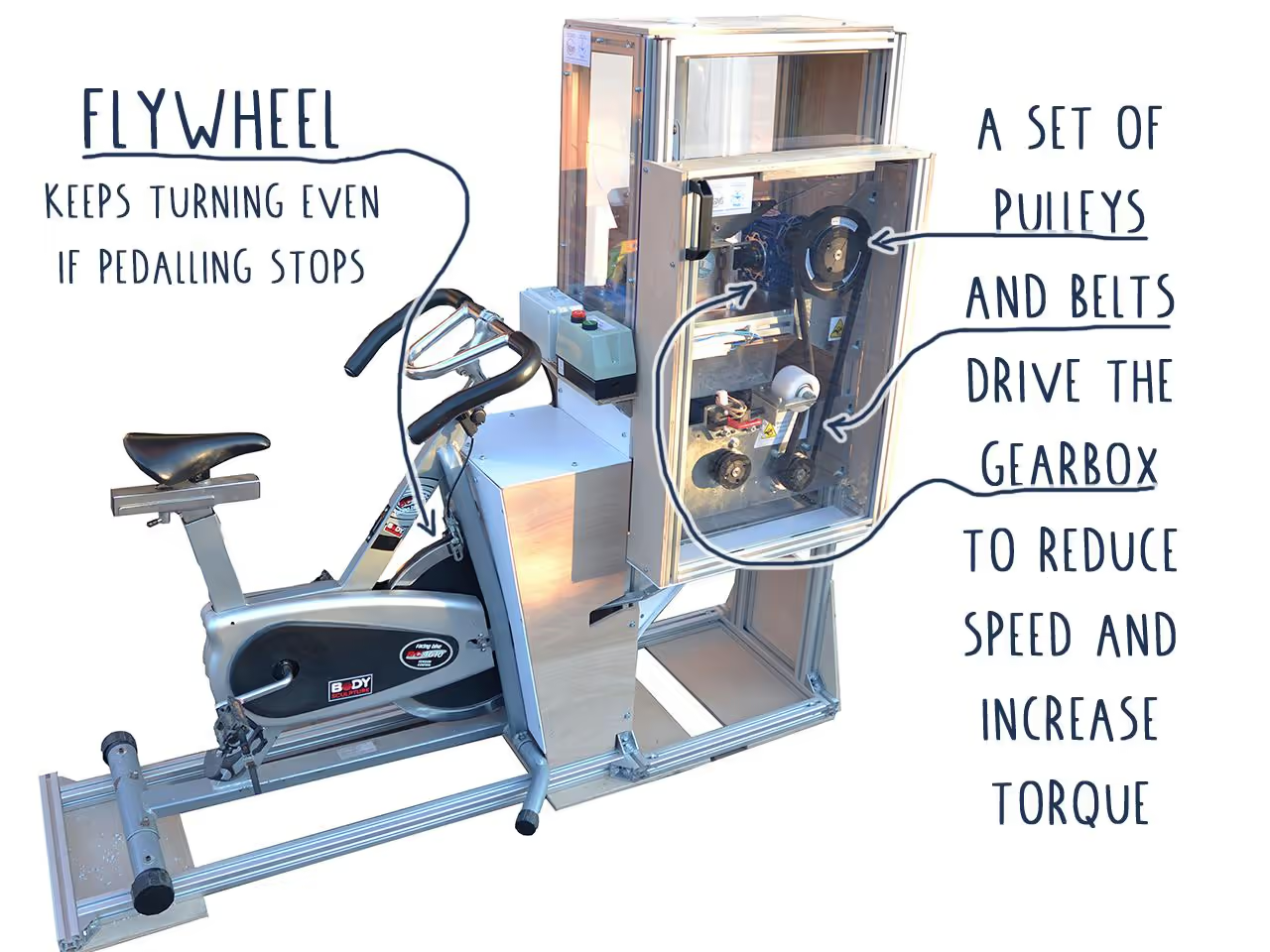
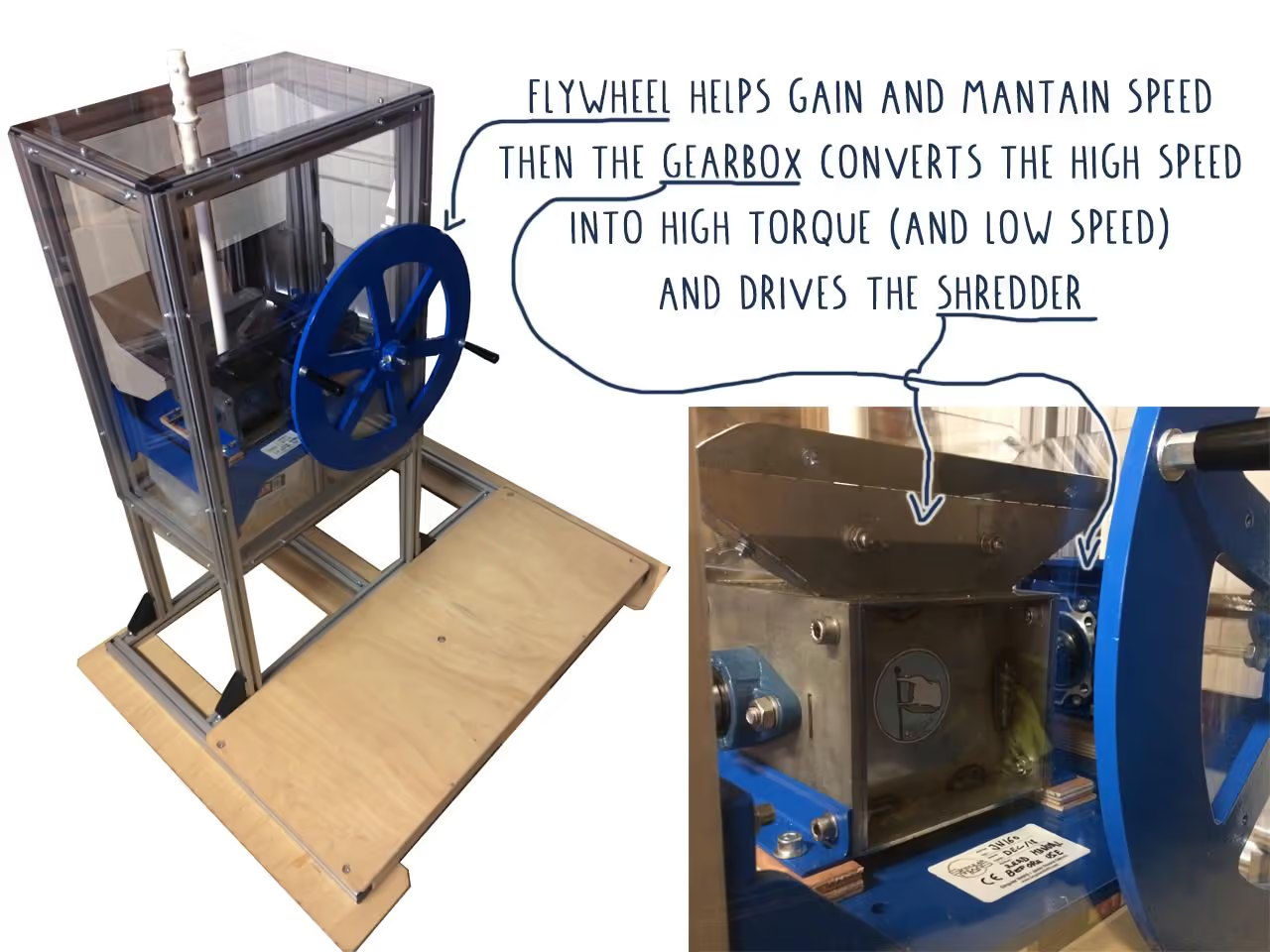
The machines are open source, allowing adaptation to your needs. If you'd prefer not to use a motor, alternative manual methods are available to power the shredder.
Table of Contents
-
This guide aims to inspire you in machine design.
We are not liable for any design or operational issues with your machine. Please consult a professional when necessary.
Adhere to all safety guidelines and practices when constructing machinery and using tools.
Proceed with designing, building, and modifying this machine at your own risk.
Note that the images and 3D models included are examples and may not suit your specific needs.
-
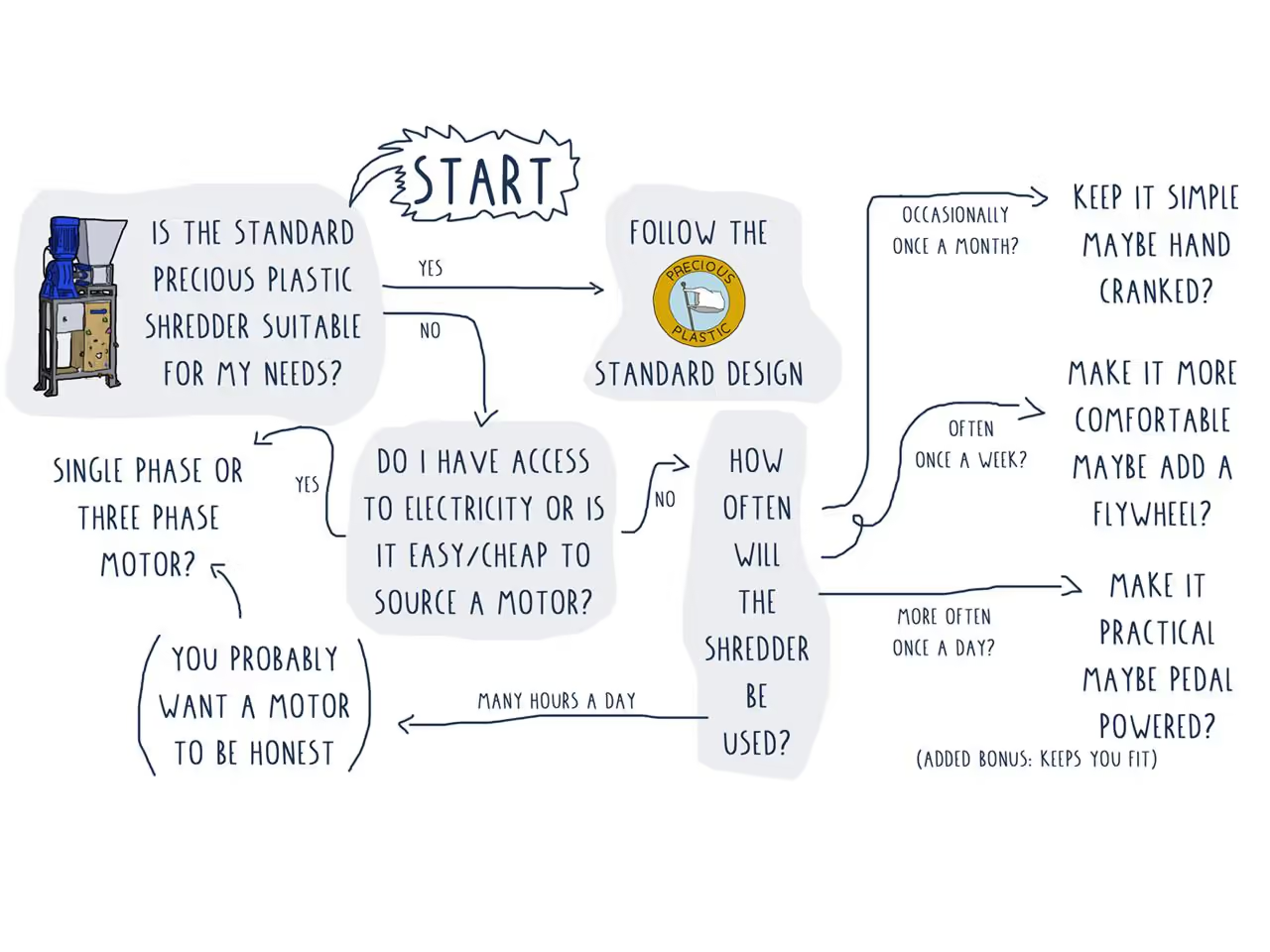
Understanding User Requirements
User Requirements Specifications (URS) are essential for defining the characteristics of a project before construction. Key considerations include:
-
Power Source: Decide between a motor (single-phase or three-phase), manual options (hand-crank or pedal), or alternative energy sources such as wind or hydro.
-
Usage Frequency: For infrequent use, a simple and inexpensive design may suffice, such as manual power. For frequent use, a more robust power source is advisable.
-
Material Availability: Utilize available resources, such as a salvaged motor or an unused exercise bike, to reduce effort and costs.
-
Skill and Process Availability: If you have welding skills, standard machine designs are feasible. Otherwise, consider outsourcing or redesigning, which could increase costs.
-
Off-Grid Use: If electricity is inaccessible, consider a non-electric design.
This structured approach ensures that decisions made at the outset guide the project effectively.
-
-
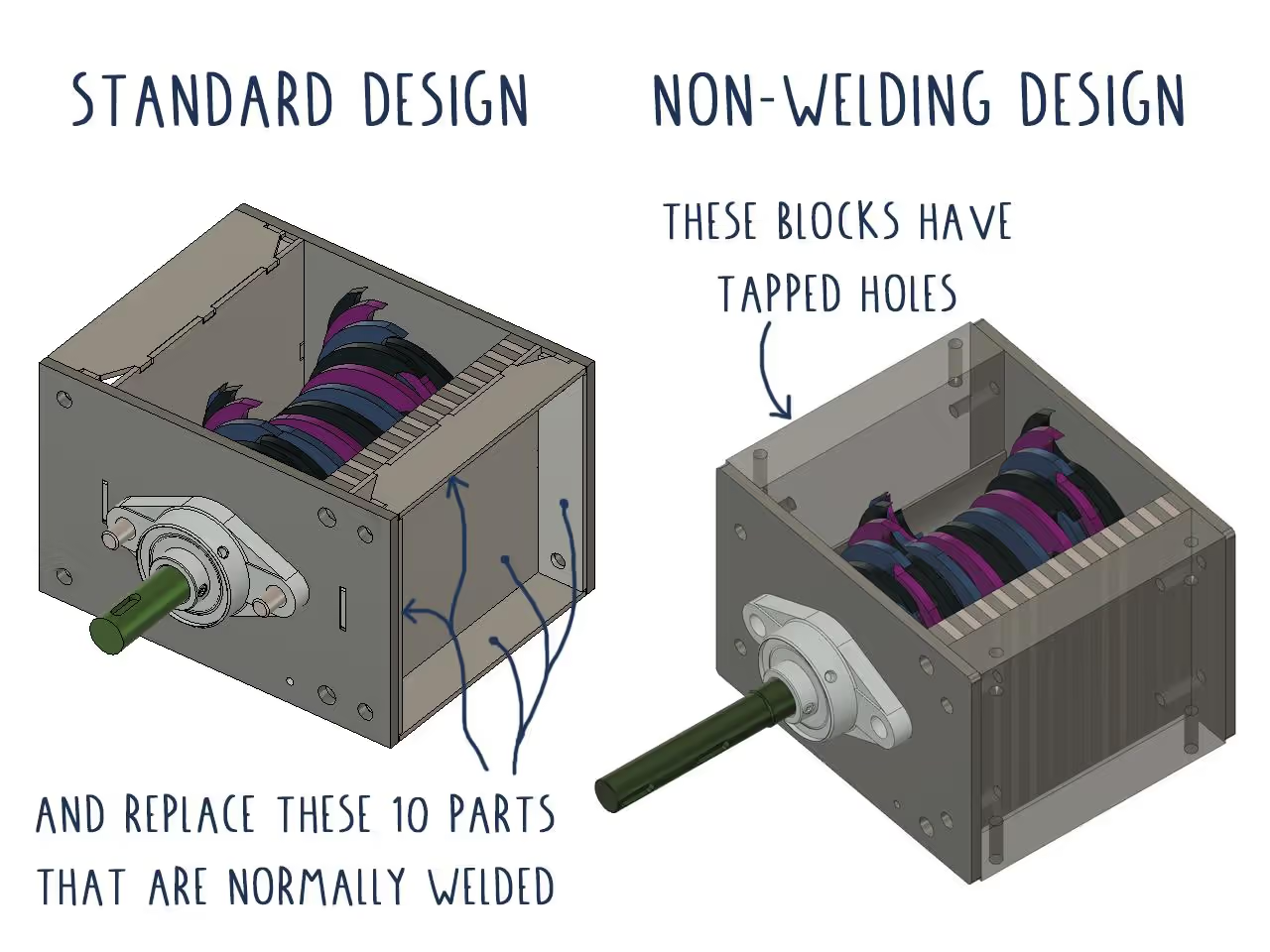
If welding steel is not an option, consider alternative methods for constructing the frame:
-
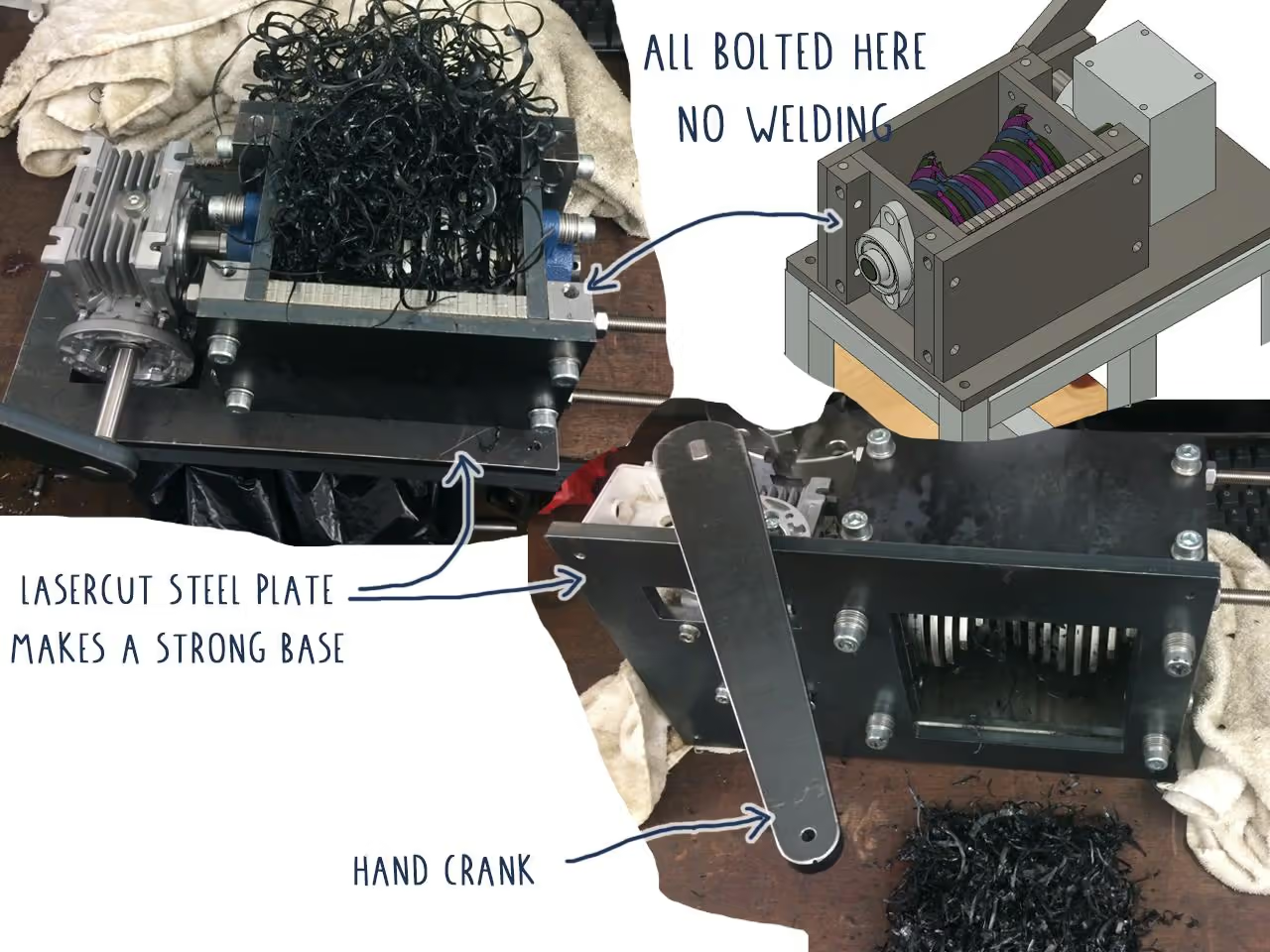
Steel sections can be joined with nuts and bolts, eliminating welding but requiring drilled holes.
-
Aluminum T-slot extrusions are also suitable; they are easy to assemble and modify.
-
Exercise caution if using wood as a structural element due to potential exposure to significant forces that wood might not withstand.
For the shredder, modifications can be made to avoid welding, but this requires precision engineering with accurately measured and squared holes and dimensions.
-
-
To enhance shredder performance, it is crucial to achieve high torque, enabling the shredding of plastics up to 1-3 millimeters (0.04-0.12 inches) with ease. The strategy involves reducing machine speed to increase torque. Power can be transmitted through various methods:
-
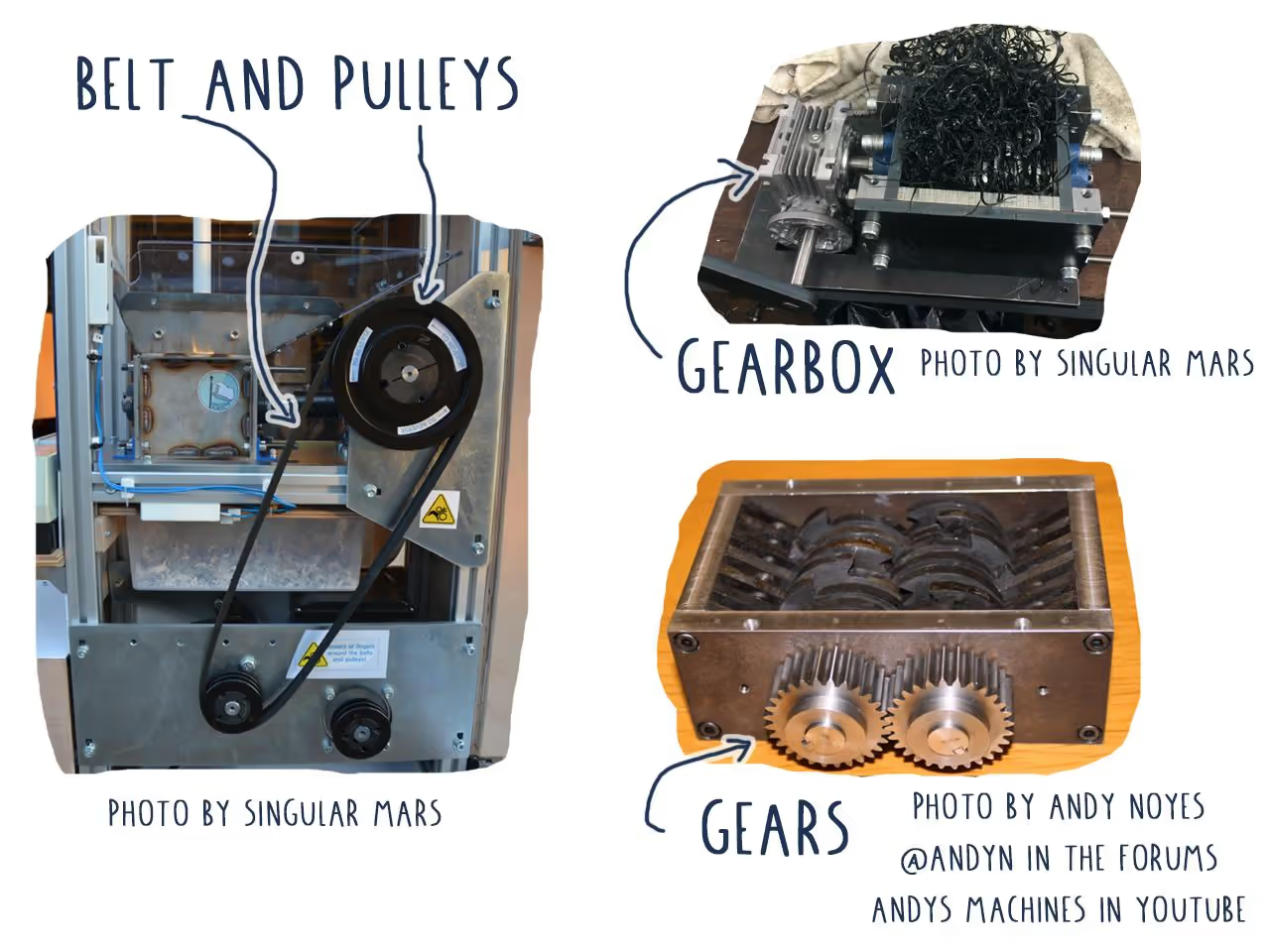
Gearbox: Compact units can reduce speed by ratios up to 100:1. They typically contain a worm gear, preventing back-driving during clogs.
-
Pulleys and Belts: These allow power transmission and can slip, which is beneficial if there's a clog.
-
Gears
-
Chains and Sprockets
-
-
Flywheels provide inertia to machines, allowing them to continue moving with minimal input. Place the flywheel on the faster side of your mechanism for optimal performance.
The efficiency of a flywheel is determined by its weight, shape, and speed. A disc or wheel shape generally works best, and distributing weight away from the axis enhances performance. Higher speeds improve the ability to maintain rotation with minimal effort.
Consider an exercise bike: the front flywheel keeps spinning even when pedaling stops.
-
Ensure the installation of guards and covers to prevent fingers from contacting any moving parts, thereby minimizing the risk of injury.
Tools
- Drill (for creating holes in steel sections)
- Welding equipment (if fabricating welded frames)
- Wrenches/bolts (for nut-and-bolt assembly)
- Precision measuring tools (e.g., calipers, squares)
- T-slot aluminum assembly tools
Software
- Open-source CAD tools (for design customization)
- 3D modeling software (for part adaptation)
- GitHub (accessing open-source machine designs)
Hardware
- Single/three-phase electric motors
- Salvaged motors or exercise bike components
- Steel sections/aluminum T-slot extrusions (structural framing)
- Gearboxes/pulleys/belts (power transmission systems)
- Safety guards/covers (for moving parts protection)
Papers
- Design and Construction of an Automated Paper Shredder with a Cross-Cut Pattern
- Design and Implementation of a Paper De-shredder
- Design and Analysis of a Paper Shredder Machine
- Design and Fabrication of Paper Shredder Machine
Opensource Designs
- Open Source Shredder v21.10
- Manual Shredder Kit
- Open Source Shredder
- SHRED-Buddy3D UPcycler
- Bicycle-Powered Shredder
- Shredder PRO by WEIMA 1.0
- Shredder 2.1